Free U.S. shipping & money back guarantee

6 min read
| March 04, 24
What Causes Yeast Infections?
Article summary
Yeast infections are caused by Candida, a type of fungus or yeast, and can affect various parts of the body including the skin, mouth, and vagina. These infections occur due to an imbalance in the body’s natural microbes, exacerbated by factors like antibiotics, hormonal changes, and a weakened immune system(1).

Why do customers love Uqora?
Innovative urinary care
Research-backed products
Money-back guarantee
Article contents
Article contents
Yeast infections are a common health concern faced by many, often accompanied by confusion, misconceptions, and a number of home remedies that can actually exacerbate discomfort. While they predominantly affect females, these infections can affect anyone(2).
Exploring the root causes of yeast infections can help us better prevent and treat them. In this article, we'll focus on vaginal yeast infections and why some people might be more prone to them.
What is a Yeast Infection?
A yeast infection, also known as candidiasis, is caused by yeast or fungus belonging to the Candida species. These infections can occur in different parts of the body.
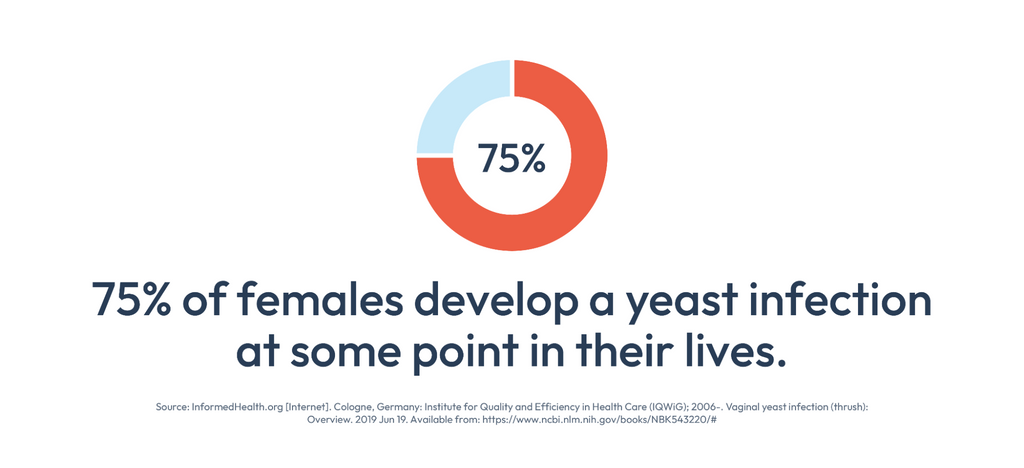
One of the most common forms is vaginal yeast infection, known as vulvovaginal candidiasis, which affects about 75% of females at some point in their lives(3).
Symptoms often include itching, burning, pain during sexual intercourse, and a thick, white vaginal discharge (1) .
In addition to vaginal yeast infections, there are other types of yeast infections to be aware of. Oral thrush, or oral candidiasis, for instance, is a common condition that develops in the mouth and is often found in babies, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems (4) .
Another relatively frequent variety is cutaneous candidiasis, which affects the skin in areas prone to moisture and warmth, like the armpits, groin, and under the breasts, leading to itchy rashes (5) .
Signs of Vaginal Yeast Infections
The typical signs of a vaginal yeast infection include (1) :
- Itching and irritation in the vagina
- Redness and swelling of the vulva and vagina
- Fragile vulva skin
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Thick, white discharge with the consistency of cottage cheese
- Pain during sexual intercourse
Causes of Yeast Infections
Candida is naturally found on our skin, in our mouths, and in our digestive tracts. This yeast usually coexists harmlessly with other microorganisms in the body.
A yeast infection arises when an imbalance allows this yeast to multiply and dominate.
The most common strain of Candida that causes yeast infections is Candida albicans. In fact, more than 90% of vaginal yeast infections are due to Candida albicans (6) . Possible causes of developing a yeast infection include (1,3) :
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics can kill bad bacteria but they can also kill off beneficial bacteria that naturally keep yeast in check. Ultimately, antibiotics can disrupt the vaginal pH balance , which could result in yeast overgrowth.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with suppressed immune systems due to conditions like HIV or undergoing treatments like chemotherapy can have a higher risk of developing yeast infections.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, menstruation, or birth control pills can alter the hormonal balance, which could increase yeast.
- Diabetes: Elevated blood sugar levels can provide an environment where yeast thrives.
- Stress: Stress can impact our bodies in many ways, and unfortunately it can also increase the risk of a vaginal yeast infection.
- Non-breathable clothing: Wearing tight clothing, underwear, or using non-breathable panty liners can create a warm and moist environment that promotes fungal growth.
- Sexual activity: . Just as the link between sex and UTIs – yeast infections can result from sexual activity too. It’s important to note that yeast infections are not a sexually transmitted infection (STI).
The Difference Between Yeast Infections, UTIs, and BV
Yeast infections, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and bacterial vaginosis (BV) are common conditions. While they might share overlapping symptoms – their causes, symptoms, and treatments differ significantly.
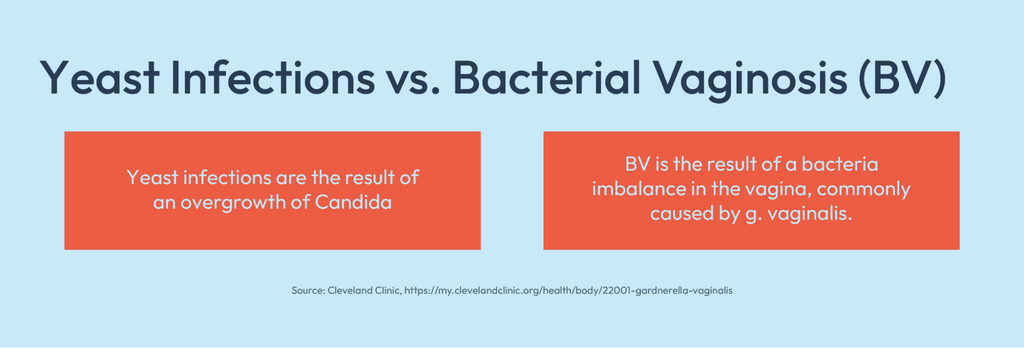
When comparing yeast infections and bacterial vaginosis, it's important to understand the differences in their causes.
While BV is caused by bacteria, yeast infections are caused by fungus.
These conditions share similar symptoms, like itching and burning during urination. However, while yeast infections cause a thick, white, odor-free vaginal discharge, BV can cause a thin, white, or gray discharge and a fishy vaginal order, especially after sex (7) .
Both yeast infections and bacterial vaginosis can also be confused for UTI symptoms. UTIs occur when a bacteria, usually E. coli , enters the urinary tract(8).
Common causes of UTIs include sexual activity, improper hygiene, and hormonal changes. UTI symptoms are commonly characterized by a strong, persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation while urinating, and dark, cloudy, bloody, or strange-smelling urine(8).
All of these symptoms are frustrating, so trying to identify what type of infection you may be dealing with can add an extra layer of frustration! That’s why it’s important to seek medical treatment if you think you are dealing with any of these infections
Tips for Preventing Yeast Infections
Remember, some people may be more prone to infections than others, so it’s important to listen to your body and seek medical treatment if you think you have an infection.
Here are some tips for preventing yeast infections (1,9,10) :
- Avoid irritants: Steer clear of harsh soaps or douching, as these can disrupt the natural vaginal balance and potentially lead to yeast infections.
- Wear breathable clothing: Opt for underwear made of natural fibers like cotton, which allows the skin to breathe and wicks away moisture from the body. Avoid tight-fitting pants and leggings for extended time periods.
- Change wet clothes: Don’t wear wet swimwear or sweaty workout clothes for too long. Moist environments can promote yeast growth – yikes!
- Manage blood sugar levels: If you have diabetes, ensure you maintain good control over your blood sugar levels. High blood sugar can feed yeast and promote its growth.
- Avoid unnecessary antibiotics: Overuse of antibiotics can kill beneficial bacteria, allowing yeast to thrive. Only take antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare professional, and always complete the full course, or as recommended from your doctor.
- Take probiotics: Vaginal probiotics can help maintain a balance of healthy bacteria in the body. Certain probiotics can even lower your risk for recurring yeast infections.
These tips can help reduce your risk but, even if it feels like you’re doing everything right – developing a yeast infection is still possible. Routine gynecological exams can help identify and address any changes or imbalances before they escalate into bigger problems. If you’re concerned about yeast infections, UTIs, or BV, schedule an appointment with your doctor as soon as possible.
Yeast Infection Causes: Frequently Asked Questions
Can a male give a female a yeast infection?
Males can carry yeast on their penis and potentially transfer it to their partner during sexual activity(3). Although yeast infections aren’t sexually transmitted infections (STI), they can be passed between partners through sexual contact.
Symptoms of yeast infections in males include itching, burning, redness, foul-smelling discharge, and more(10). A male who has a yeast infection can pass it to a female partner during intercourse.
Using condoms can reduce the risk of transferring yeast between partners. However, other factors can make a person susceptible to a yeast infection after sex, such as hormone changes, antibiotic use, or a weakened immune system.
Are yeast infections contagious?
Yeast infections are not “contagious” in the same way a flu or cold is. However, the yeast responsible for the infection can be transferred between individuals under certain circumstances. As mentioned, the yeast can spread between sexual partners during vaginal, oral, or anal intercourse(3).
Similarly, oral thrush can be passed between individuals through close contact like kissing, especially if one person has an active infection. However, just because the yeast is transferred doesn’t mean it will result in an infection. Various factors can increase susceptibility, like a weakened immune system(4).
Can certain foods cause yeast infections?
Food doesn’t directly cause yeast infections. In fact, some dietary habits can help maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms in the body. Foods that are rich in probiotics promote a healthier gut microbial ecosystem(9). Including foods rich in saturated fatty acids, like cheese, in your diet may also hinder the growth of Candida in the gut(11) .
Can dirty fingers cause a yeast infection?
Fingers can introduce bacteria to the vagina, potentially triggering a yeast infection by disrupting the balance of microbes(12). Bacteria from dirty fingers can also lead to bacterial infections like BV and urinary tract infections. We know you know – but make sure you, or your partner, washes their hands before putting them near your vagina.
Can antibiotics cause a yeast infection?
Antibiotics are a potential cause of yeast infections because they disrupt the microbial balance in the body. Antibiotics kill bacteria of all kinds, including the beneficial bacteria that naturally keep yeast in check. When these bacteria are eliminated, yeast can multiply quickly, leading to an infection(1). Probiotics could help with maintaining a healthy balance of bacteria during antibiotic treatment(13).
Final Notes
Yeast infections are common and treatable, but as you know, they can cause significant discomfort and disrupt your daily life. Understanding the various yeast infection causes is crucial for prevention and management.
Promoting overall well-being is vital for preventing these infections. For vaginal yeast infections for example, it’s important to take steps to support your sexual and urinary health. Ensuring your urinary and vaginal health is in a good place may help reduce the risk of yeast infections and other related conditions.
Note: references to "female", “women”, “male”, and “men” in this article refer to sex assigned at birth, not gender.
This article does not replace medical advice. We recommend you seek treatment if you think you are experiencing a UTI.
References
- Vaginal yeast infection: Causes, symptoms & treatment. (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved December 21, 2023, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/5019-vaginal-yeast-infection
- Yeast infection. (n.d.). Yale Medicine. Retrieved December 21, 2023, from https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/yeast-infection
- InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. Vaginal yeast infection (thrush): Overview. 2019 Jun 19. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK543220/
- Oral thrush—Symptoms and causes. (n.d.). Mayo Clinic. Retrieved December 21, 2023, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/oral-thrush/symptoms-causes/syc-20353533
- Candidiasis (Yeast infection)—Skin disorders. (n.d.). Merck Manuals Consumer Version. Retrieved December 21, 2023, from https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/skin-disorders/fungal-skin-infections/candidiasis-yeast-infection
- Superti F, De Seta F. Warding Off Recurrent Yeast and Bacterial Vaginal Infections: Lactoferrin and Lactobacilli. Microorganisms. 2020 Jan 17;8(1):130. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8010130. PMID: 31963487; PMCID: PMC7023241.
- Bacterial vaginosis (Bv): Causes, symptoms & treatment. (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved December 21, 2023, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/3963-bacterial-vaginosis
- Urinary tract infection(Uti). (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved December 21, 2023, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9135-urinary-tract-infections
- Spinillo A, Capuzzo E, Nicola S, Baltaro F, Ferrari A, Monaco A. The impact of oral contraception on vulvovaginal candidiasis. Contraception. 1995 May;51(5):293-7. doi: 10.1016/0010-7824(95)00079-p. PMID: 7628203.
- Male yeast infection (Candida balanitis): Symptoms, causes & treatment. (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved December 21, 2023, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23199-male-yeast-infection
- Jeziorek M, Frej-Mądrzak M, Choroszy-Król I. The influence of diet on gastrointestinal Candida spp. colonization and the susceptibility of Candida spp. to antifungal drugs. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2019;70(2):195-200. doi: 10.32394/rpzh.2019.0070. PMID: 31215785.
- Medical News Today. (2019, August 7). Yeast infection after sex: What to know. Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326110
- Fernández-Alonso M, Aguirre Camorlinga A, Messiah SE, Marroquin E. Effect of adding probiotics to an antibiotic intervention on the human gut microbial diversity and composition: a systematic review. J Med Microbiol. 2022 Nov;71(11). doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001625. PMID: 36382780. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36382780/
